GFM Market Process
Natural Gas Futures Market (GFM) Contracts
GFM trades are executed via the contracts established by EXIST. Definitions regarding the market process are given below:
- Financial Period (Trade Interval)
This is the period which differs for each contract and during which bids can be placed and matches can be made. Futures market contracts are closed for trading before physical delivery
- Delivery Period
This is the period, which differs for each contract and during which bidding ends and the physical delivery obligation arising from the match is fulfilled. An equal amount is delivered on each gas day covered by the relevant futures market contract.
- Contract
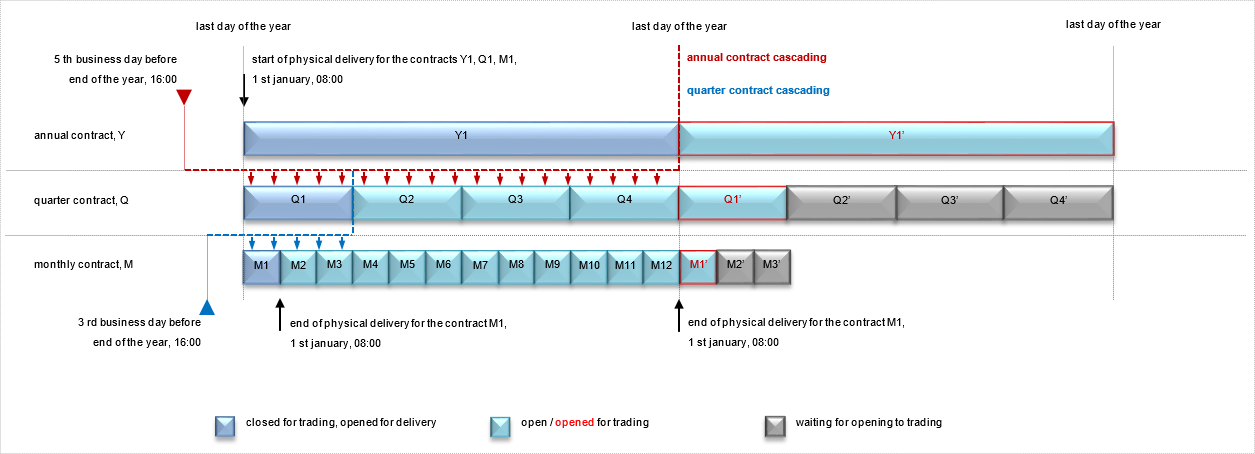
The contract is a standardized contract that creates an obligation to take delivery of/deliver the matching amount of natural gas and to pay/receive the matching amount for each gas day of the relevant delivery period. Contracts are named with the delivery period. In the Futures Market, there are currently “12 monthly, 4 quarterly and 1 annual contract” created by EXIST.
a. Monthly Futures Contracts
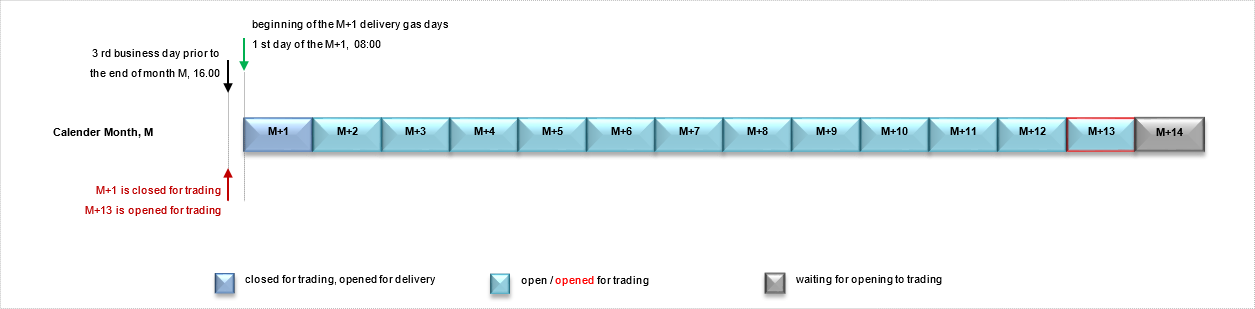
Twelve monthly contracts are traded on the futures market at the same time. At 4:00 p.m. on the three days before the last business day of the current month, the contract for the following month is closed and the contract for the thirteenth month is opened for trading. The obligation for physical delivery of a contract starts on the first gas day and ends on the last gas day of the month in which the contract is named.
b. Quarter Futures Contracts
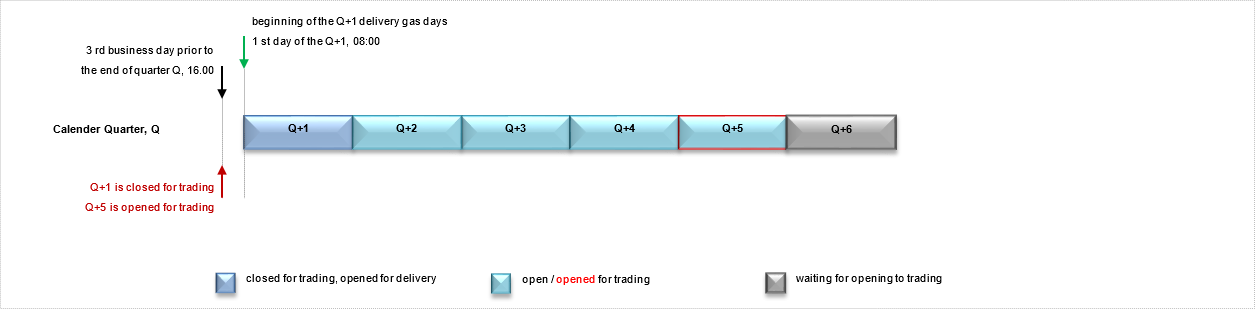
The futures market trades 4 quarterly contracts at the same time. At 16.00 on the third day before the last business day of the current quarter, the following quarter contract is closed and the following fifth quarter contract is opened for trading. The physical delivery obligation of the matches in a quarterly contract starts on the first gas day and ends on the last gas day of the quarter in which the contract is named.
First Quarter Contract covers January-February-March, Second Quarter Contract covers April-May-June, Third Quarter Contract covers July-August-September and Fourth Quarter Contract covers October-November-December.
c. Annual Futures Contracts
One annual contract is traded on the futures market at a time. At 04:00pm on the fifth business day before the last day of the current year, the contract for the following year is closed and the contract for the second following year is opened for trading. The physical delivery obligation of the matches realized in a one-year contract starts on the first gas day and ends on the last gas day of the year in which the contract is named.

Daily Operation of Futures Market
A trading day in the Natural Gas Futures Market is consisted of four parts:
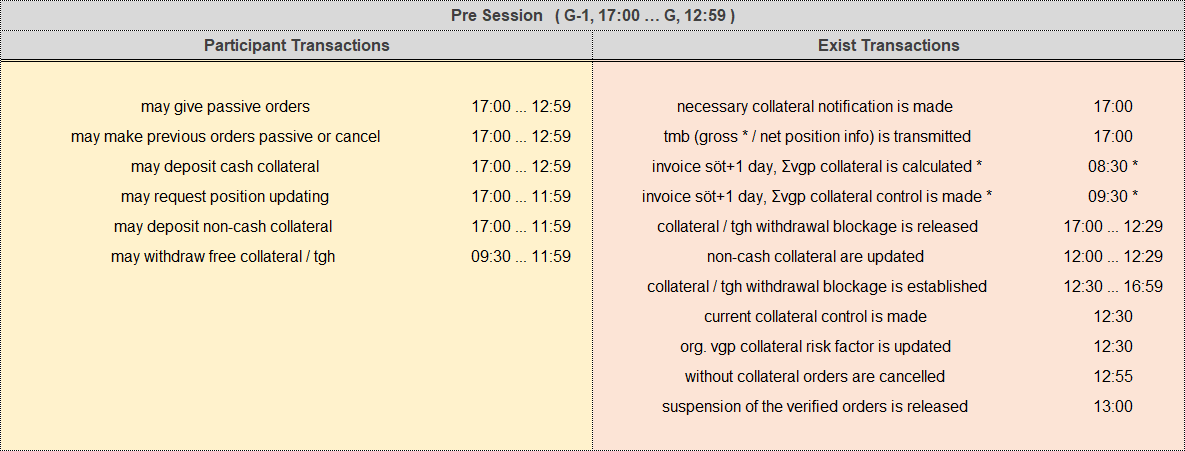
a.pre-session
Pre-Session processes are listed in the table below and, in the table, yellow background indicates participant capabilities, red background indicates EXIST capabilities, the sign (*) indicates capabilities with intervals longer than the gas day.
b. intra-session
Intra-session processes are listed in the table below and, in the table, yellow background indicates participant capabilities, red background indicates EXIST capabilities, the sign (*) indicates capabilities with intervals longer than the gas day.

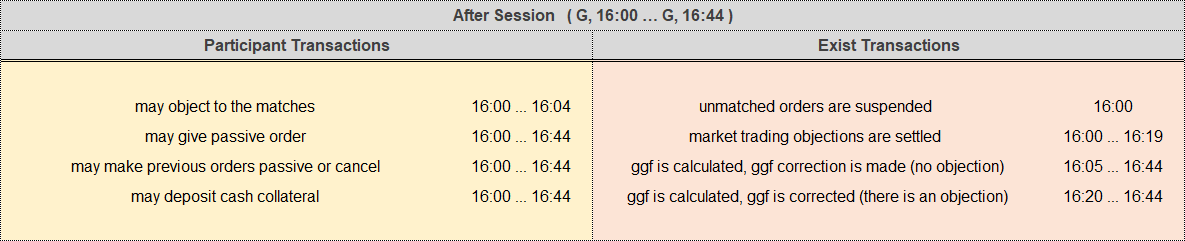
c. after-session
After-Session processes are listed in the table below and, in the table, yellow background indicates participant capabilities, red background indicates EXIST capabilities, the sign (*) indicates capabilities with intervals longer than the gas day.
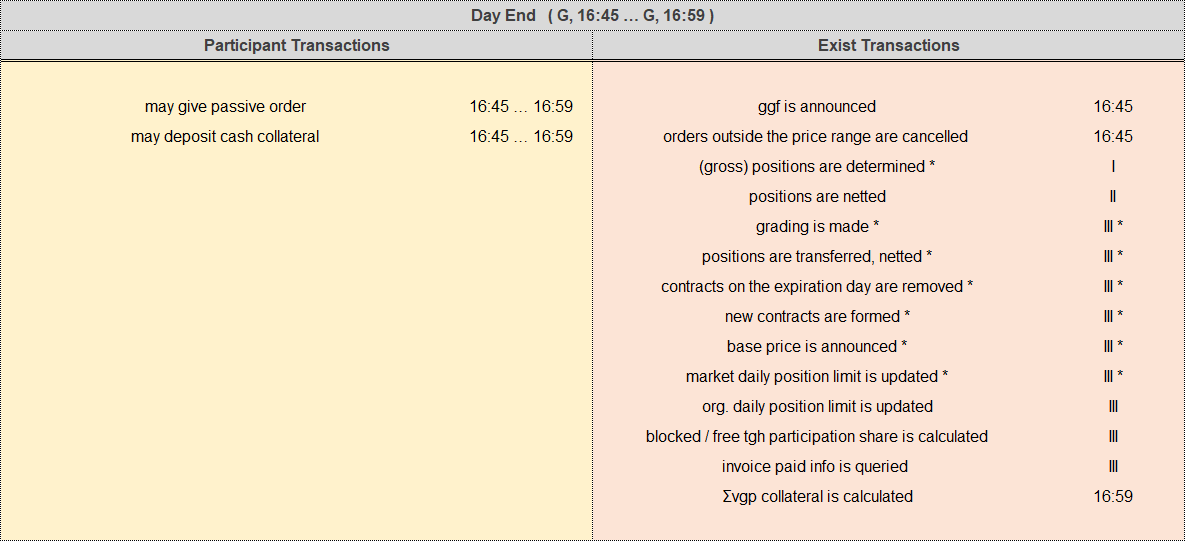
d. day end-session
End-of-Day processes are listed in the table below and, in the table, yellow background indicates participant capabilities, red background indicates EXIST capabilities, the sign (*) indicates capabilities with intervals longer than the gas day.
Order and Matching
When a participant who completed the registration process makes an order in the Natural Gas Futures Market, it triggers matching and all other processes (collateral, settlement, invoicing). Hence, the order and matching process will be discussed first.
Characteristics of Order
For registration of the orders given in the futures market, the following conditions should be fulfilled:
1. Order Quantity
Order quantity can be given in 1 lot (1000.Sm³) and its multiples. The “user buy/sell quantity limit” defined by the Shipper Admin user and the market limit defined by EMRA are limited to 10.000 lots/day.
2. Order Price
Order price can be given in 0.01 TRY/1000.Sm³ and its multiples. The Shipper is limited to the “user buy/sell price limit” defined by the Admin user and the “market price limit (order minimum/maximum price)” determined for the relevant month according to EMRA legislation.
3. Types of Order
Orders in the futures market are given in four different types:
a.Standard (STD)
This is an order placed in the order book according to the priority of price and time of entry in the order book and ends at contract close.
b.Time-out (SUR)
This is an order which is entered in the order book according to the priority of price and time of entry in the order book and expires at the defined expiry time.
c. Match What is Available and Destroy (OEYE)
This is an order which is not in the order book and immediately matches the eligible counter-offer partially, if any, and the rest is cancelled, and otherwise terminates.
d. Immediate or Cancel (TEYE)
This is an order which is not in the order book and immediately matches the eligible counter order exactly, if any, and otherwise it terminates.
Order Limits
For registration of orders given in the futures market, the following conditions should be fulfilled:
- The order price for each futures contract is limited to ± 5% of the opening price (“base price” on the first day of the contract, “daily indicator price (GGF)” on other days).
- The order amount in each futures contract is limited to the position limit of the participant. This value is calculated by applying the participant’s organized market entry and exit allocation share to the market position limit. It is taken as 500,000 Sm3/day for the existing participants below 500,000 Sm3/day and for participants who will trade in the Turkish natural gas market for the first time.
Order and Priority Rules
The following controls are executed after the registration of the participant’s order, i.e. entering a new order, updating an existing order or activating an inactive order:
a. The order with the lowest price in the Sell direction and the highest price in the Buy direction has priority and is placed at the top of the order book among orders in the same direction.
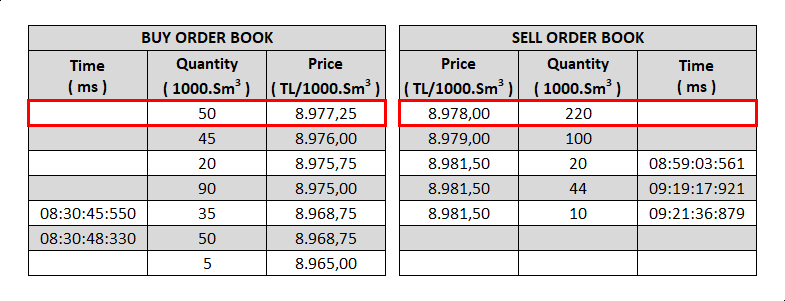
b. Among orders with the same price, the first one recorded in the order book has priority. (Orders are recorded in the order book with a unique number and at least ms precision.)
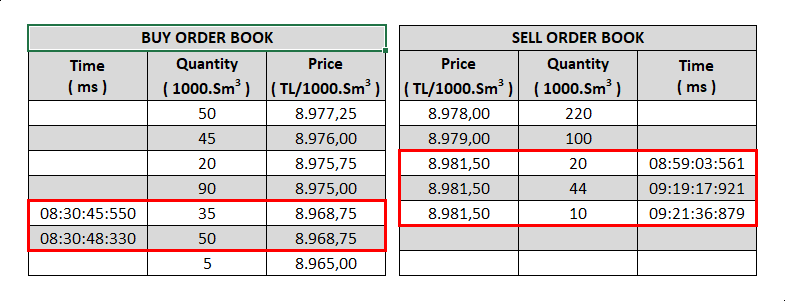
c. Price or quantity changes, participant or system cancellations, expiry of order or contract validity periods after the order is registered in the order book all will cause the order to be updated with the new version number and processing time.
d. Reduction in the quantity of existing orders is not considered an update and the time of entry of the order is not changed.
2. The market participant can update, cancel or change the status of the order to active-passive as long as it is not matched. An order remains in the book until its validity period expires or the relevant contract is closed.
Matching and Priority Rules
After recording the participant’s order, i.e. entering a new order, updating an existing order or activating an inactive order, the following controls are made:
1.If the best sell order price is higher than the best buy price, the match does not occur and continues to wait in the book.
2. If the price of the best sell order is equal to the price of the best buy order, a match occurs. The match price is the same as the price of the orders. The quantity is evaluated according to points (4) and (5).
3. If the best sell order price is lower than the best buy order price, a match occurs. The matching price is the price of the order recorded in the book first. Quantity evaluation is done according to items (4) and (5).
To express these three rules differently, in order for orders to match, there must be no price difference between them, they must meet at the same value in the event that “the seller lowers the price and/or the buyer raises the price” or they must extend to the other side in the event that “the seller underbids the buyer and the buyer overbids the seller”. Meeting at the same price occurs when one party records its order in the order book in advance and the other party accepts it, while extension occurs when the parties record their orders in close time without seeing each other’s orders.
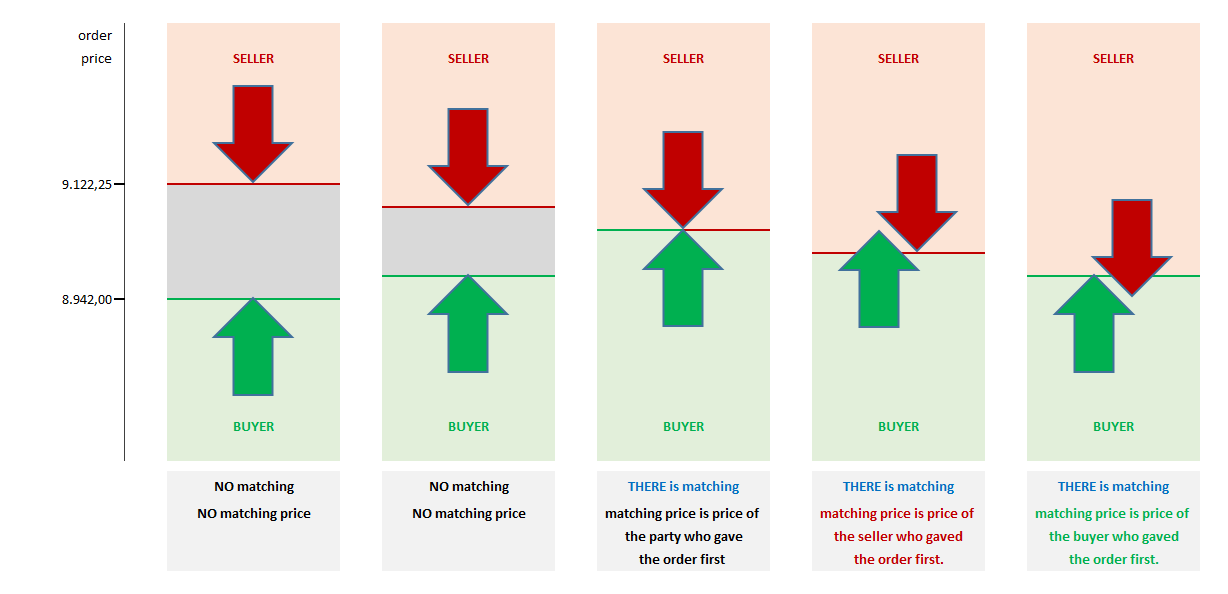
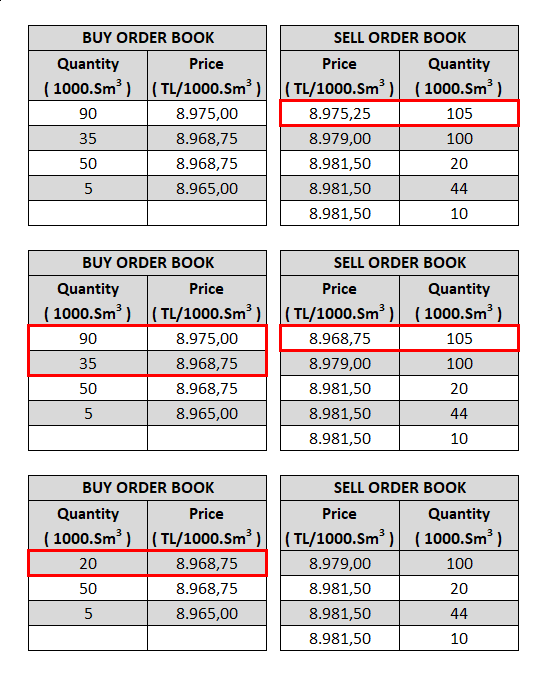
4. The match quantity is the smaller quantity of the orders. The order with the larger quantity is partially matched and will remain in the order book with the remaining quantity and price until the end of the order or contract period.
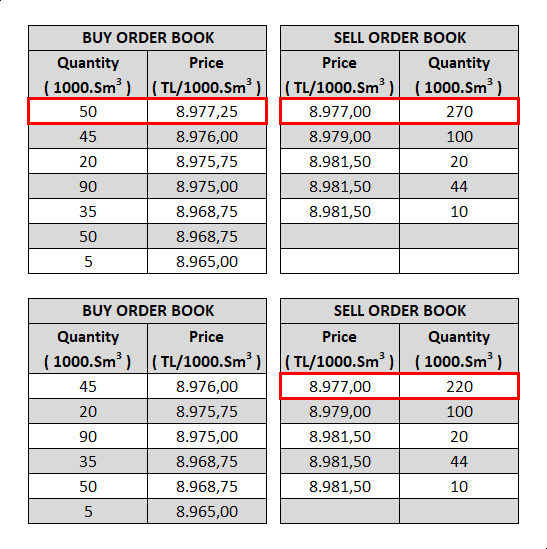
5. The large quantity order is re-matched with the first ranked order in the opposite direction if quantities and prices comply. This continues until the compliance of the quantity and price left from the opposite directional orders ends.
Results of the Matching
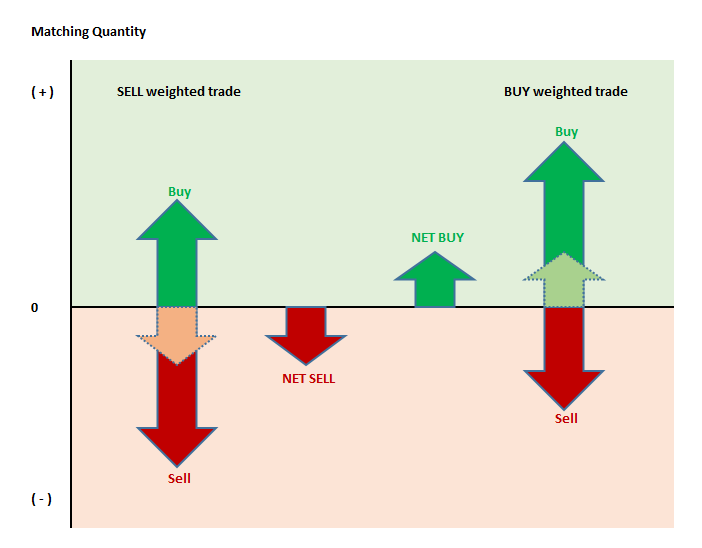
1.After the orders are matched, the relevant amounts become “positions” for the participants.
A participant whose buy order is matched becomes holder of a “long position” and a participant whose sell is matched becomes a holder of “short position”. A participant’s position in a contract at any point in time is determined by the difference between the sum of the buy match amounts and the sum of the sell match amounts and is defined as a “net or open position”.
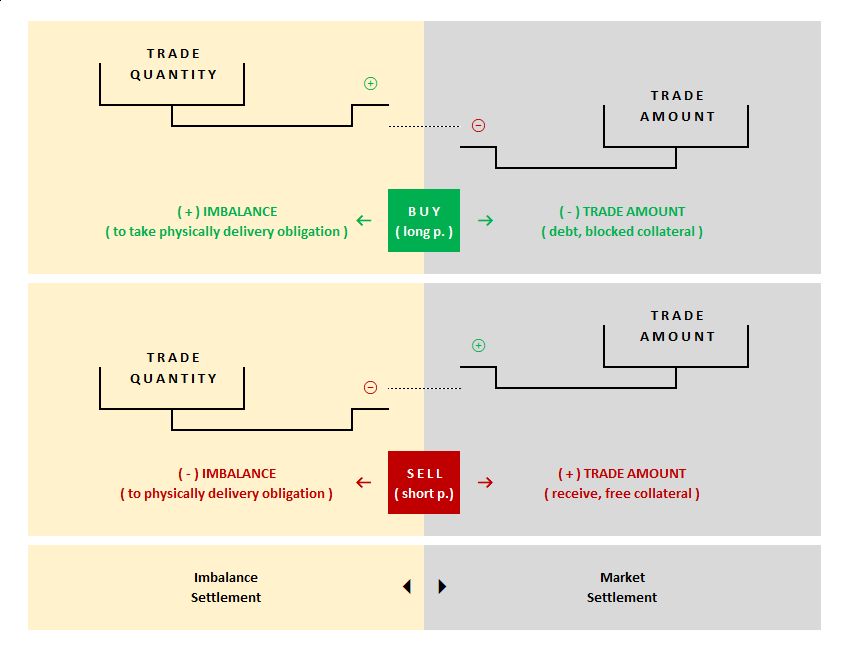
2. The matching quantities give rise to a physical delivery obligation to the participant when the delivery period arrives.
Each match changes the size of the participant’s “open position” and, depending on the situation, its “direction”. When the contract is closed and the delivery period starts, the participant is obliged to take delivery of the relevant amount of natural gas if the final direction is positive (buy) and deliver it if it is negative (sell).
3. When the existing open position is fully covered by a reverse match of the same quantity before the expiry of the contract, the obligation of the participant for physical delivery is eliminated.
After the expiry of the contract, the open position shall be closed by delivery or receipt of natural gas. When this condition is not met, the participant falls into imbalance and this situation is taken into account in collateral calculations.
4. After the orders are matched, the relevant amounts become “credit or debit” for the participants.
For the participant, the matched buy-side orders create “debit” and sell-side orders create “credit”. These amounts are reconciled daily during the relevant billing period and notified to the participant as collateral.
5. The weighted average of the matched orders in each contract is calculated instantaneously and reported to the market.
Weighted Average Price (WAP) is the instantaneous average price calculated by dividing the total trading volume (sum of matching amounts) of a contract by the sum of matching quantities. This data is updated after each match in the relevant contract line as a benchmark for participants to take into account in their orders.
AOF = [ ( M1 . F1 + M2 . F2 + … + MN . FN ) / ( M1 + M2 + … + MN ) ] instant
Every order and every match in the GFM change the price calculations in the relevant contract. The weighted average price calculated at the close of the session is called the Daily Indicative Price (DIP). This price is used to calculate the margin required to be held by market participants for their positions at the end of the session and to determine the price range in which the relevant contract can be traded for the next day.
Netting Positions and Full Spread
In order to determine the delivery and collateral obligations of the participant, the difference between the buy match quantities and the sell match quantities in the same contract is called “netting”.
In order to determine the collateral obligations of the participant, the difference between the buy match amounts and sell match amounts in different contracts covering the same gas days is called “full spread”.
“Grading” is performed by transferring the positions in the closed annual contract to four quarterly contracts and the positions in the closed quarterly contract to three monthly contracts. The physical delivery obligation is determined according to the net position in the monthly contracts.
Confirmation of Trade
After the orders match, EXIST notifies the participating parties instantly (optionally via SMS and/or e-mail) that their orders have been matched and confirmed. Thus, the participant can see his/her finalized match without the counterparty’s knowledge.
Objection to Trade
1.Participants have 15 minutes from the trade confirmation notification to file an objection, but not later than 5 minutes after the close of the session. Objections will only be accepted if they are filed in due time and the error is caused by EXIST.
2. If the objection period expires or the objection is deemed unjustified by EXIST, the trade confirmation becomes valid and becomes a contract within the framework of the contract. A participant not objecting within the time limit shall be considered to have accepted the trade confirmation in its entirety.
3. The amount to be collected per objection found unjustified is determined by the Board Resolution and added to the participant’s market operation fee.
4. In case of a large number of objections regarding a contract, EXIST may announce to the participants that it suspends the relevant contract after evaluation.























